-
Research Article
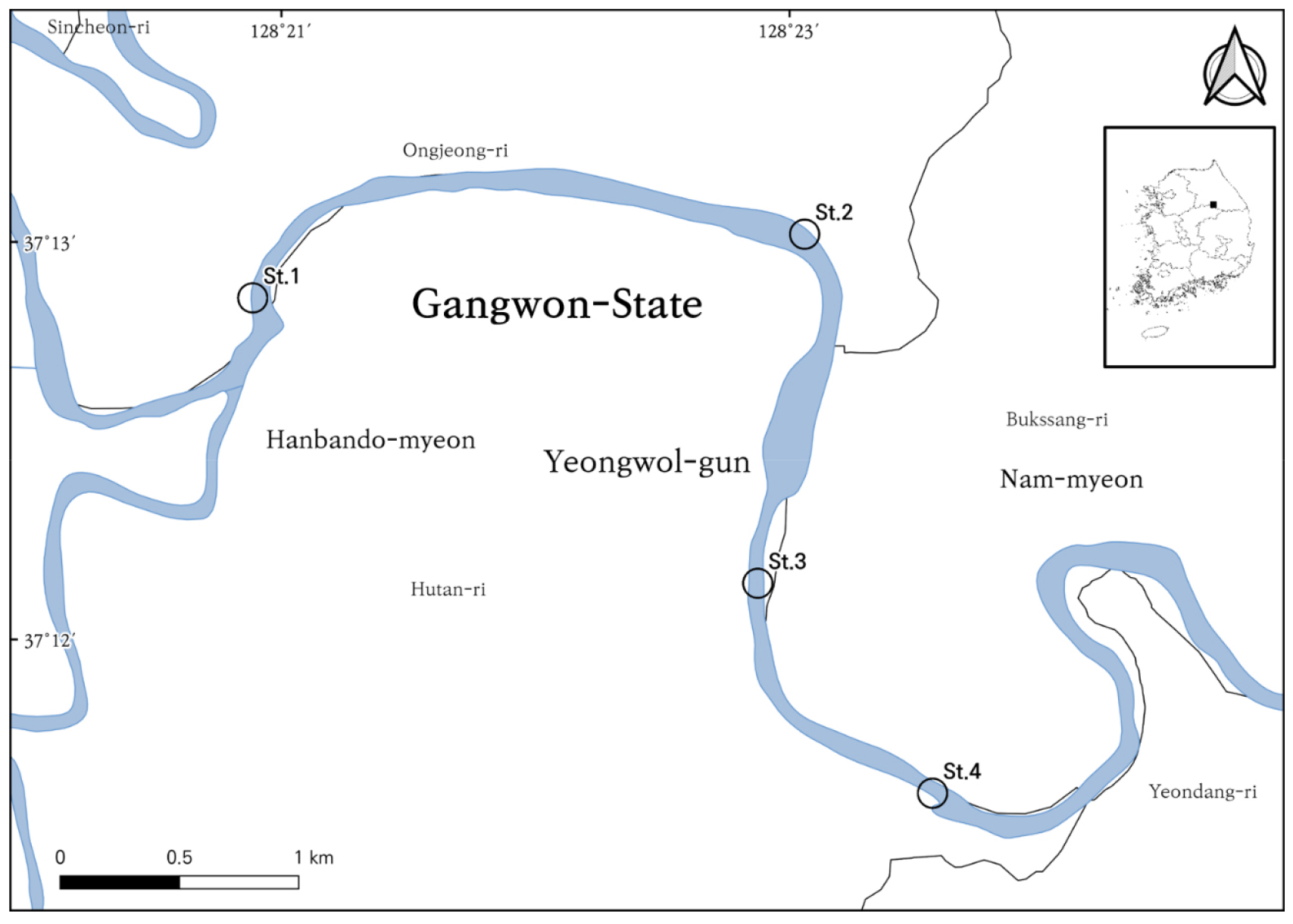
- Fish Community Structure and Population Ecology of the Endangered Gobiobotia brevibarba in Pyeongchang River, Korea
- Seung-Chul Park, Doupyo Hong, Jaehoon Kim, Jaeseok Choi
- This study, conducted from September 2022 to April 2023, analyzed the fish community composition and population characteristics of Gobiobotia brevibarba in the …
- This study, conducted from September 2022 to April 2023, analyzed the fish community composition and population characteristics of Gobiobotia brevibarba in the Pyeongchang River, Yeongwol, demonstrating this riverine ecosystem’s ecological conservation value. The survey identified 2,157 individuals across 23 species belonging to 8 families in the Pyeongchang River. Notably, 17 species (74.0%) were classified as Korean endemic species, significantly exceeding the national average. This suggested that the aquatic environment of the Pyeongchang River is well preserved from anthropogenic disturbances and maintains excellent naturalness. The presence of 5 nationally protected species-Acheilognathus signifer, Pseudopungtungia tenuicorpa, Hemibarbus mylodon, Gobiobotia macrocephala, and G. brevibarba (all designated Class II Endangered Wild Animals by the Ministry of the Environment)-further emphasized the importance of the Pyeongchang River for biodiversity conservation. G. brevibarba was the dominant species, suggesting the Pyeongchang River offers an optimal habitat. Analysis of the rank-abundance models of the fish community revealed a distinct pattern: the Preemption, Zipf, and Log-normal models best described upstream (St.1-2), midstream (St.3), and downstream (St.4) sites, respectively. This indicated a clear upstream-to-downstream increase in species richness, evenness, and ecological stability. Such spatial heterogeneity is closely related to differences in habitat characteristics (e.g., current velocity and substrate structure) across river sections, reflecting the provision of preferred habitats for fish of different age classes. Detailed analysis of the G. brevibarba population showed positive allometric growth (b-value > 3.0) in the length-weight relationship, indicating favorable growth conditions for the Pyeongchang River G. brevibarba population. Additionally, the von Bertalanffy growth model estimated an asymptotic length (L∞) of 163.1 mm and a Brody growth coefficient (k) of 0.32, indicating high growth potential. The observed size distribution and growth parameters clearly demonstrated that G. brevibarba in the Pyeongchang River forms a healthy, self-sustaining, and stable population. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
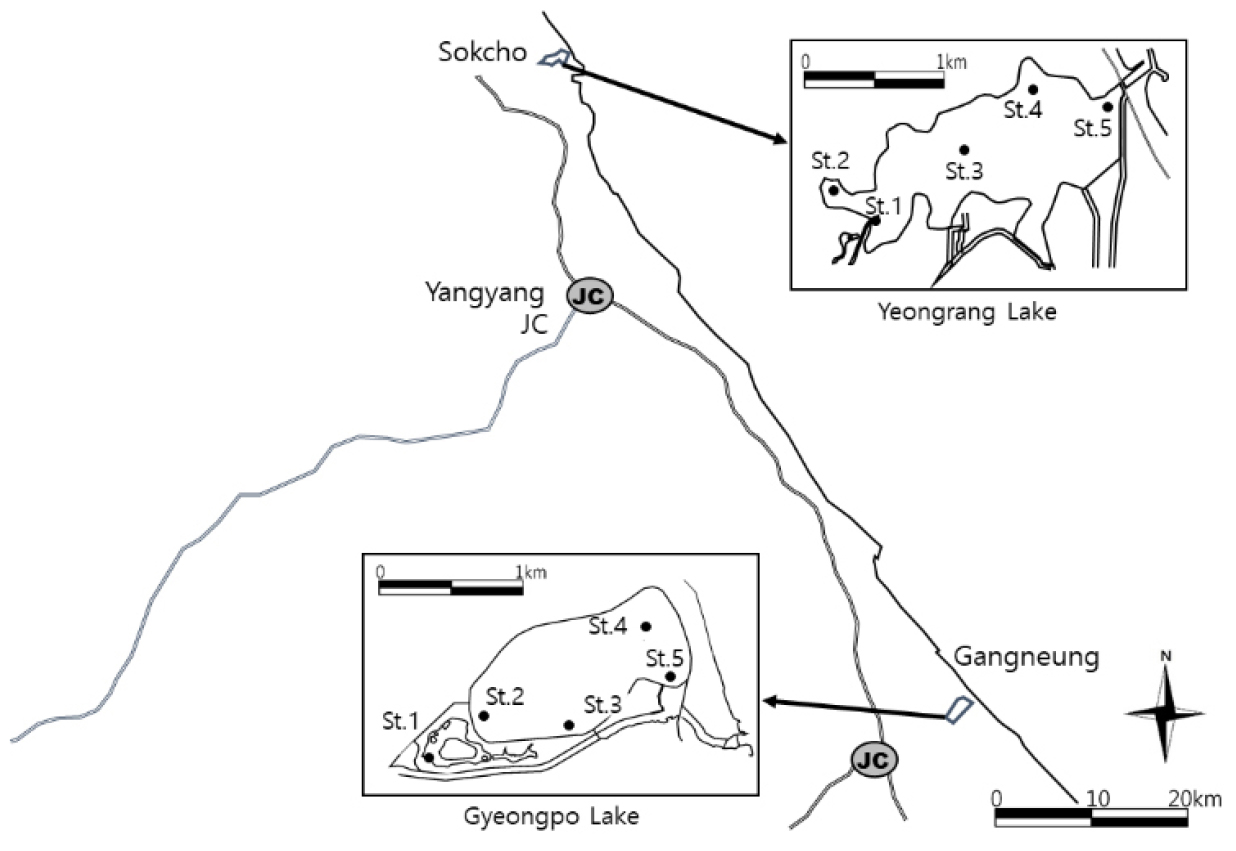
- Seasonal Influence on the Relationship between Fish and Piscivorous Birds in the Yeongrangho and Gyeongpoho Lagoons under Environmental Change
- Heonwoo Park, Hyojae Park, Jaeyong Lee, Jaeseock Choi
- In this study, we aimed to compare and analyze piscivorous bird and fish communities in the Yeongrangho and Gyeongpoho Lagoons, two representative …
- In this study, we aimed to compare and analyze piscivorous bird and fish communities in the Yeongrangho and Gyeongpoho Lagoons, two representative lagoons on the East Coast of Korea, and to elucidate the impacts of environmental changes on their ecosystem composition. Yeongrangho showed higher species diversity, with 42 fish species identified, compared to 25 species in Gyeongpoho. However, the total number of individuals in Gyeongpoho (10,671) was approximately three times higher than that in Yeongrangho (3,478). Gyeongpoho had a concentration of individuals of a few specific species, such as Konosirus punctatus (gizzard shad). Meanwhile, Yeongrangho maintained higher diversity with a relatively even distribution of individuals among species. This reflects the difference between Gyeongpoho’s stable brackish water environment and high productivity and Yeongrangho’s increased artificial seawater exchange and ongoing marinification. The number of piscivorous birds tended to be proportional to the total number of fish. In Gyeongpoho, where the fish abundance was significantly higher, the number of piscivorous birds, especially Phalacrocorax carbo, was higher than that in Yeongrangho. This confirms that food availability is a crucial factor that influences the distribution and abundance of top predators such as piscivorous birds. In lagoons, physical environmental factors, such as water depth, salinity, transparency, and freezing, along with anthropogenic interventions, that is, seawater exchange and pontoon bridge installation in Yeongrangho and wetland restoration in Gyeongpoho, had complex influences on the fish and bird communities. Enhanced seawater exchange in Yeongrangho accelerated the marinification of the fish community. Meanwhile, wetland restoration in Gyeongpoho has likely contributed to the expansion of bird habitats and increased food availability for piscivorous birds. East coastal lagoons commonly face environmental challenges such as eutrophication due to nutrient inflow, which can affect the entire food web. The findings emphasize the importance of tailored conservation and management strategies that consider the ecological characteristics of each lagoon and the impacts of anthropogenic interventions. A sustainable approach that prioritizes the maintenance of ecosystem health and function rather than only development is essential. This study provides important baseline data for understanding the interrelationship between piscivorous bird and fish communities in Yeongrangho and Gyeongpoho. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

- Reaching Carbon Neutrality in Agriculture: Applications of Hydrogen Energy in the Agricultural Sector
- Moon Kyung Kang
- Climate change and rising greenhouse gas emissions pose urgent global challenges, prompting intensified policy measures and technological innovations to achieve carbon neutrality. …
- Climate change and rising greenhouse gas emissions pose urgent global challenges, prompting intensified policy measures and technological innovations to achieve carbon neutrality. Following the 2015 Paris Agreement, the transition to renewable energy sources has accelerated globally, with hydrogen energy emerging as a promising alternative for a sustainable energy future. Major economies, including the United States, EU, Japan, and China, have incorporated comprehensive hydrogen-based technologies across energy, transportation, and industry sectors. However, agriculture, particularly agricultural machinery, has seen limited integration, despite its significant contribution to emissions. Addressing this gap requires expanded research, investment, and commercialization efforts. In the Republic of Korea, hydrogen integration into smart farming has started with various demonstration projects, but commercial viability remains constrained by insufficient research and supportive policy frameworks. This study assesses global carbon neutrality initiatives and hydrogen energy strategies, exploring potential applications within the Republic of Korea’s agricultural machinery sector. The work is intended to advance the development and adoption of hydrogen energy, contribute toward carbon neutrality goals, and promote innovation and sustainable development in agriculture. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
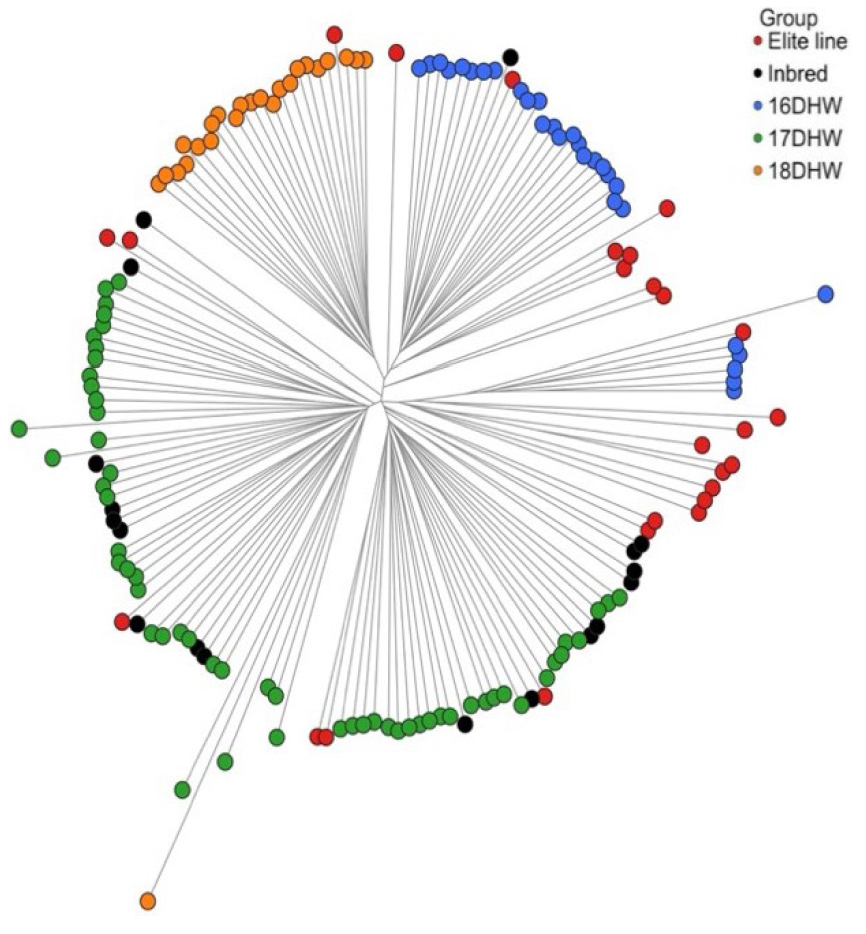
- Molecular Characterization of Doubled Haploid Lines Informs Core SNP Panel Selection in Waxy Maize
- Seung-Hyun Wang, Si-Hwan Ryu, Min Namgung, Jung-Heon Han, Jae-Keun Choi, Hee-Sun Noh, Hye-Lim Choi, Yong-Jin An
- Doubled haploid (DH) technology accelerates the development of inbred lines but can also reduce genetic diversity and extend long-range linkage disequilibrium. We …
- Doubled haploid (DH) technology accelerates the development of inbred lines but can also reduce genetic diversity and extend long-range linkage disequilibrium. We profiled 155 waxy maize lines encompassing DH groups, elite lines, and conventional inbreds using genome-wide SNPs to quantify population structure and to develop a practical core SNP panel. Linkage disequilibrium decay was summarized using in 50 kb distance bins up to 5 Mb, and population structure was assessed using Nei’s genetic distance, principal coordinate analysis (PCoA), and nearest-neighbor purity. Three core marker selection strategies were compared for core panels: Shannon-index-based selection, random sampling with genetic distance optimization, and genetic/physical map-balanced binning. Across the collection, nearest-neighbor purity reached 86.5%, far exceeding a randomized baseline of 23.5% ± 3.9%, supporting the presence of a well-defined group structure. Elite lines showed the highest diversity (He = 0.315; 1,432 group-specific alleles), whereas one DH set (18DHW) exhibited the lowest diversity across most indices. Random sampling with genetic distance optimization (RS) yielded a 21-SNP panel that achieved 99.98% pairwise discrimination among 155 lines, the SI method delivered a compact 10-SNP set maximizing diversity metrics, and binning produced 30/39/47-SNP panels providing uniform chromosomal coverage. Collectively, the results support a hybrid strategy—RS for maximal discrimination and bin-based markers for genome-wide coverage—as the most practical design for fingerprinting and core-collection development in maize breeding. The selected panel will be implemented in genotyping assays for cross-laboratory validation and transferability testing on external germplasm. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
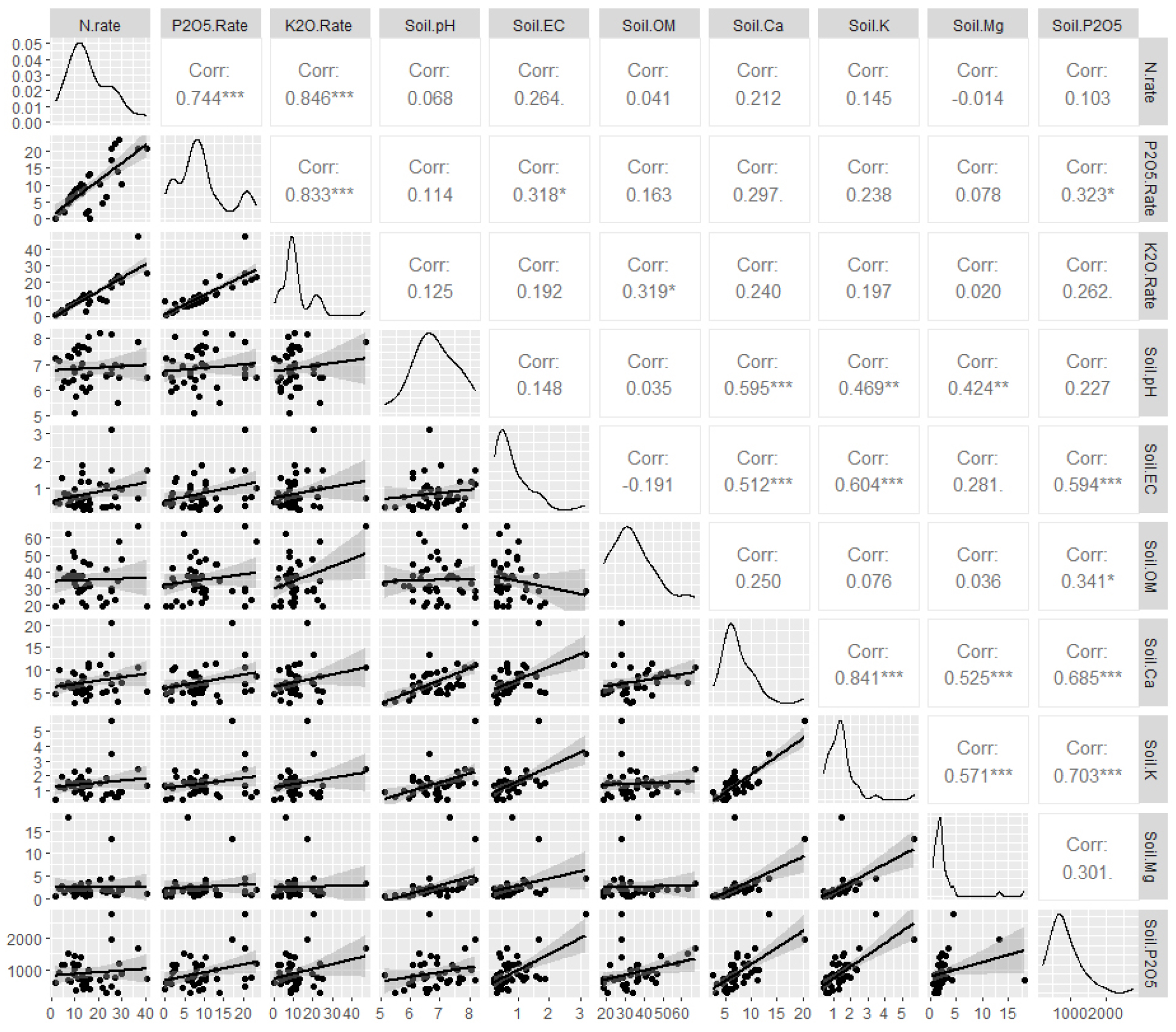
- Effect of NPK Fertilization Rates on Soil Chemical Properties, Crop Productivity and Nutrient use Efficiency in Wild Chive (Allium monanthum Maxim.)
- Dong-Min Kim, Min-Gyeong Kim, Seong-Yu Hong, Soo-Young Hong, Hee-Yeon Kim, Soo-Jeong Heo, Ki-Sun Kim, Ye-Jin Lee
- The effects of NPK fertilization levels on soil chemical properties, plant growth and nutrient use efficiency were evaluated in cultivated wild chive …
- The effects of NPK fertilization levels on soil chemical properties, plant growth and nutrient use efficiency were evaluated in cultivated wild chive (Allium monanthum Maxim.). Cultivation experiments were conducted over two years (2023-2024) at five fertilization levels (0×, 0.5×, 1.0×, 1.5×, and 2.0×) based on the standard rate of 111-67-107 kg・ha-1 (N-P2O5-K2O). Additionally, a fertilizer use survey was conducted on 41 major cultivation farms. The survey revealed that available phosphate and exchangeable potassium levels in many cultivated soils tended to exceed the recommended ranges. In the cultivation experiment, fertilization exceeding the standard rate reduced dry matter yield, whereas the maximum yield was achieved at 79-113-90 kg・ha-1 (N-P2O5-K2O), as revealed by regression analysis. The highest crop productivity and nutrient use efficiency were observed at 0.5-1.0× the standard fertilization rate. Fertilizer use efficiency indices (FPFP, FAE, and FR) were also highest within this range. These results indicate that rational fertilizer management can help maintain soil nutrient balance and promote sustainable cultivation of wild chives. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
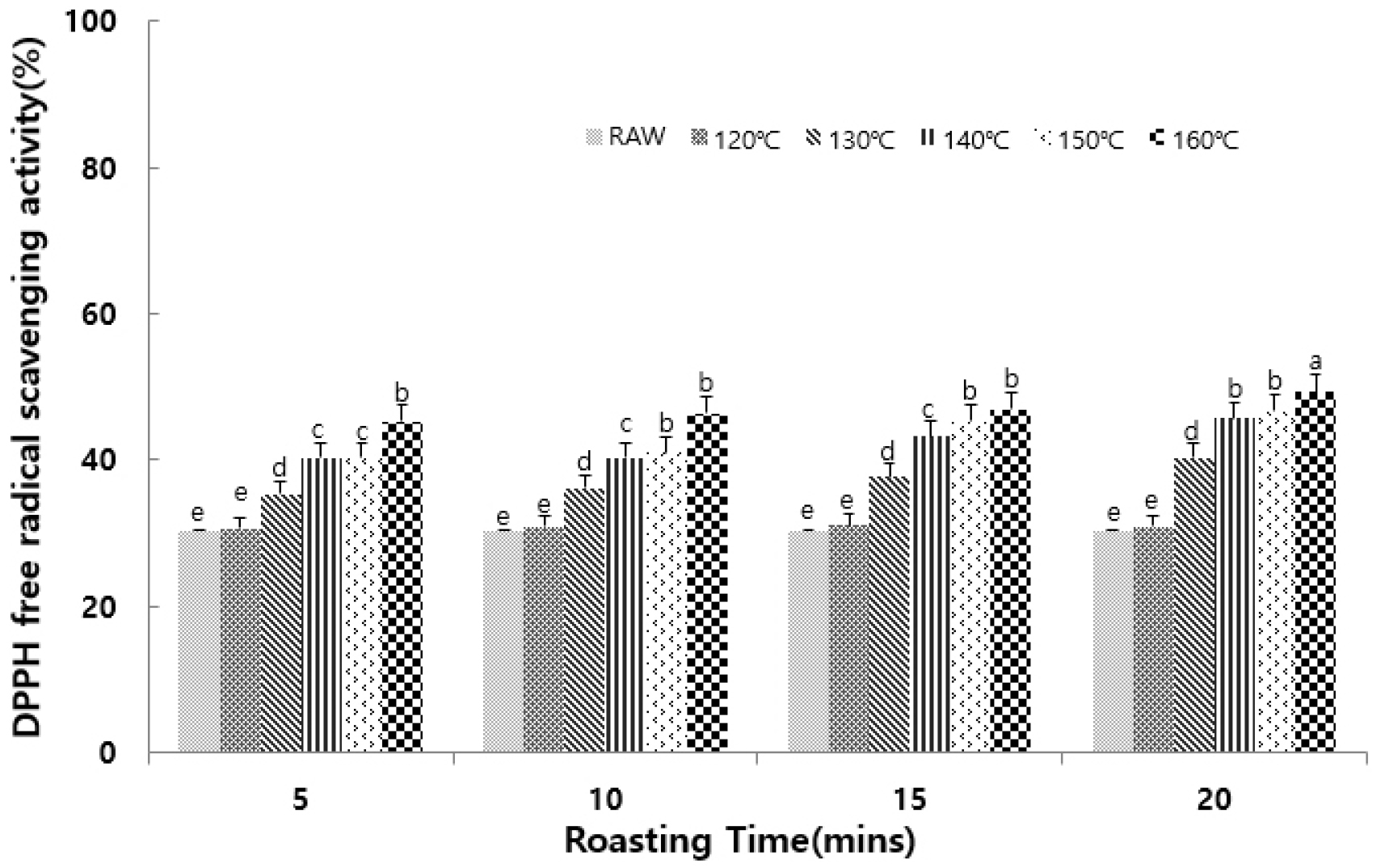
- Establishing Roasting Conditions for Optimizing the Antioxidant Activity of Seoritae
- Sung-Jin Park, Ye-bin Kang, Hyo-Eun Ban, Bo-Hye Kim, Seong-Jun Kim
- The aim of this study was to provide basic data for the production of processed products using Hongcheon Seoritae. The characteristics …
- The aim of this study was to provide basic data for the production of processed products using Hongcheon Seoritae. The characteristics and antioxidant activity of roasted Seoritae were measured by varying the roasting temperature (120, 130, 140, 150, and 160°C) and roasting time (5, 10, 15, and 20 min), followed by evaluation of the product quality. With increasing roasting temperature and time, the brightness (L*) of the roasted Seoritae powder decreased, while the redness (a*) and yellowness (b*) increased. Additionally, the moisture content and pH both decreased significantly with increasing roasting temperature and time. The highest total anthocyanin content was detected in the untreated Seoritae (0.75 mg/g), but this decreased significantly to 0.24-0.70 mg/g as the roasting temperature and time were increased. No significant differences were observed for the total polyphenol and total flavonoid contents with varying roasting temperatures and times. The antioxidant activity, as determined using DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging assays, tended to increase with higher roasting temperature and time, with the highest antioxidant activity being observed at 160°C after 20 min of roasting. Based on these results, further studies should focus on sensory evaluations and response surface methodology to identify the optimal roasting conditions that maintain high levels of bioactive compounds without compromising sensory preference. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
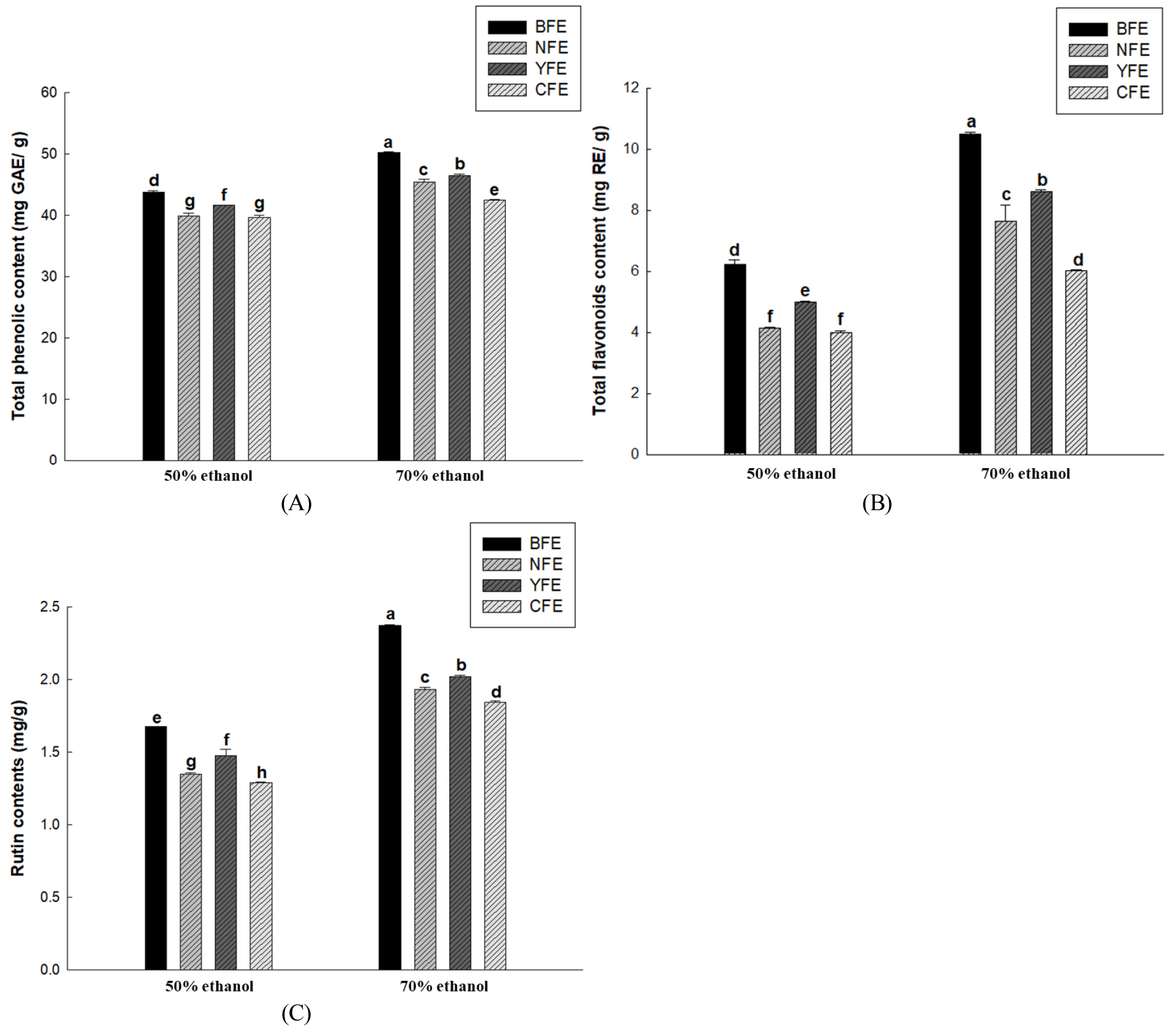
- Comparative Analysis of Proximate Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Fagopyrum esculentum from Different Origins and Optimization of Extraction Conditions
- Hyun-Woo Oh, Geun-Hee Cho, Young-Jae Heo, Aram Song, Gun Kim, Sang-hyeon Park, Jae-Jin Lee, Sun-Il Choi
- Fagopyrum esculentum, widely cultivated worldwide, is a functional crop rich in phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and rutin, all of which have strong …
- Fagopyrum esculentum, widely cultivated worldwide, is a functional crop rich in phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and rutin, all of which have strong antioxidant properties. However, the extraction efficiency of these bioactive compounds is affected by extraction conditions and cultivation origin. This study examined three domestic F. esculentum cultivars (Bongpyeong, Nonsan, Yecheon) and one Chinese cultivar to establish optimal extraction conditions and compare antioxidant capacities. Extraction parameters included ethanol concentration (50% and 70%) and temperature (40°C, 60°C, and 80°C), while extraction time was fixed at 2 h. Total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), and rutin content were quantified, while antioxidant activity was evaluated using DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging assays, FRAP, and reducing power. Results showed that extraction using 70% ethanol at 40°C yielded the highest TPC, TFC, and rutin recovery across all cultivars. Among samples, Bongpyeong F. esculentum extract consistently exhibited the strongest antioxidant activity, followed by the Yecheon, Nonsan, and Chinese varieties. Antioxidant activities increased dose dependently, with significant differences among cultivars (p & 0.05). These variations were closely associated with origin- and cultivar-specific differences in bioactive composition. In conclusion, the antioxidant potential of F. esculentum is strongly influenced by extraction conditions and cultivation origin. The optimized condition (70% ethanol, 40°C, and 2 h) maximized recovery of phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and rutin, particularly in the Bongpyeong cultivar. These findings provide a scientific basis for extraction standardization and underscore the importance of the cultivar and origin when developing F. esculentum as a functional food material. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
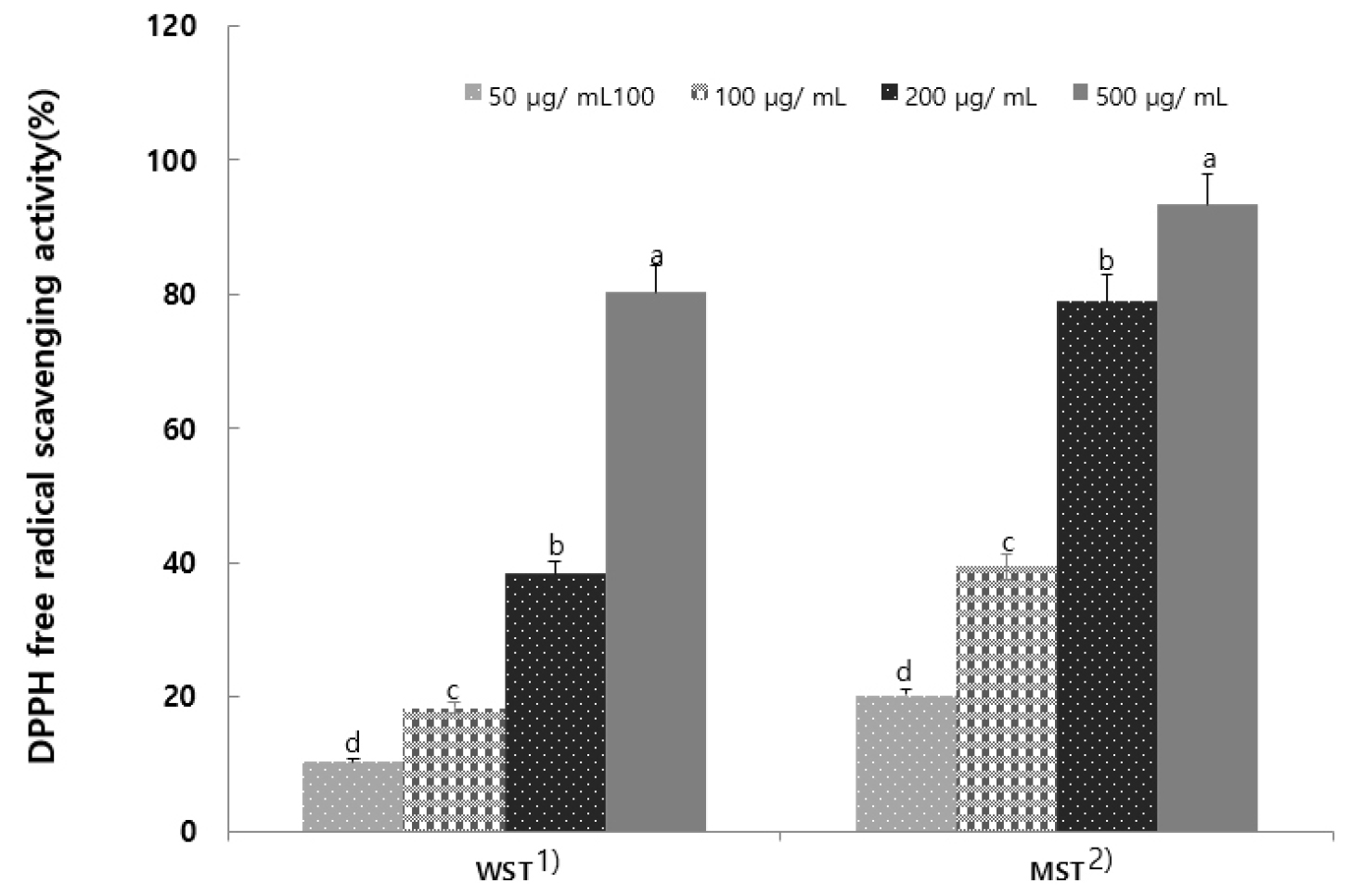
- Chemical Properties and Antioxidant Activity of Selaginella tamariscina Leaf Extract
- Eon Hwan Shin, Seok-won Lee
- This study was performed to determine whether Selaginella tamariscina leaf can be used as a natural health food source by measuring the …
- This study was performed to determine whether Selaginella tamariscina leaf can be used as a natural health food source by measuring the proximate and antioxidative nutrients. The contents of carbohydrate, crude protein, crude fat, and crude ash were 66.03%, 13.20%, 1.32%, and 12.24%, respectively, and the total dietary fiber content was 31.25%. The hot-water extract (WST) and 80% methanol extract (MST) activities in S. tamariscina were also evaluated, which showed that the total polyphenol and total flavonoid contents of WST and MST were 43.25 ± 8.32 mg/g and 67.32 ± 5.20 mg/g and 12.33 ± 0.09 mg/g and 16.80 ± 3.64 mg/g, respectively. The whitening effect was measured based on tyrosinase inhibitory activity, which was 95.0% at 500 µg/mL in the 80% MST. Finally, WST and MST demonstrated significant antimicrobial activity. These results suggest that extracts from the S. tamariscina leaf could be used to develop potent antioxidant and antimicrobial agents and may be useful as ingredients for new functional food additive materials. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
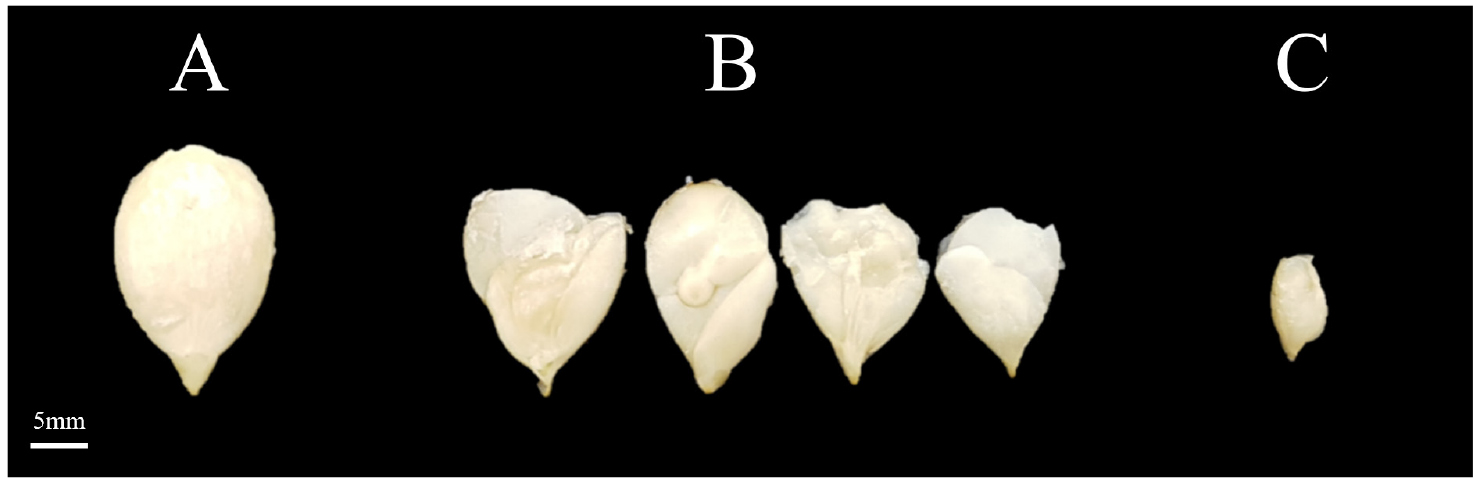
- Characteristics of Hybrid Individuals Resulting from the Hybridization of Cucurbita maxima and Cucurbita moschata
- Paulin Lee, Sung Min Park
- Interspecific hybridization between Cucurbita maxima and C. moschata was conducted to improve fruit quality, storability, and agronomic performance. This study evaluated morphological …
- Interspecific hybridization between Cucurbita maxima and C. moschata was conducted to improve fruit quality, storability, and agronomic performance. This study evaluated morphological and physicochemical traits of selected F1 hybrid progenies, including fruit weight, length, diameter, flesh thickness, total soluble solids (TSS), and color parameters (L*, a*, b*). Significant variation was observed among combinations. The 15-19-7S × 3-8-2 cross produced the largest fruits (1.97 kg), while 3-3-1 × 15-11-2S showed compact morphology and stable internal structure. Notably, 15-21-2S × 5-1-1 exhibited the highest TSS (16.28 °Brix) and vivid yellow coloration, indicating high carotenoid content. Among tested genotypes, 3-3-1 × 15-11-2S was most suitable for general market needs due to balanced size and quality, while 15-21-2S × 5-1-1 showed enhanced sweetness and functional properties. Fruit set limitation in interspecific hybrids was alleviated using 2,4-D at 50-500 ppm. These findings suggest the potential of interspecific hybridization for developing high-quality winter squash cultivars with enhanced consumer traits and breeding utility. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
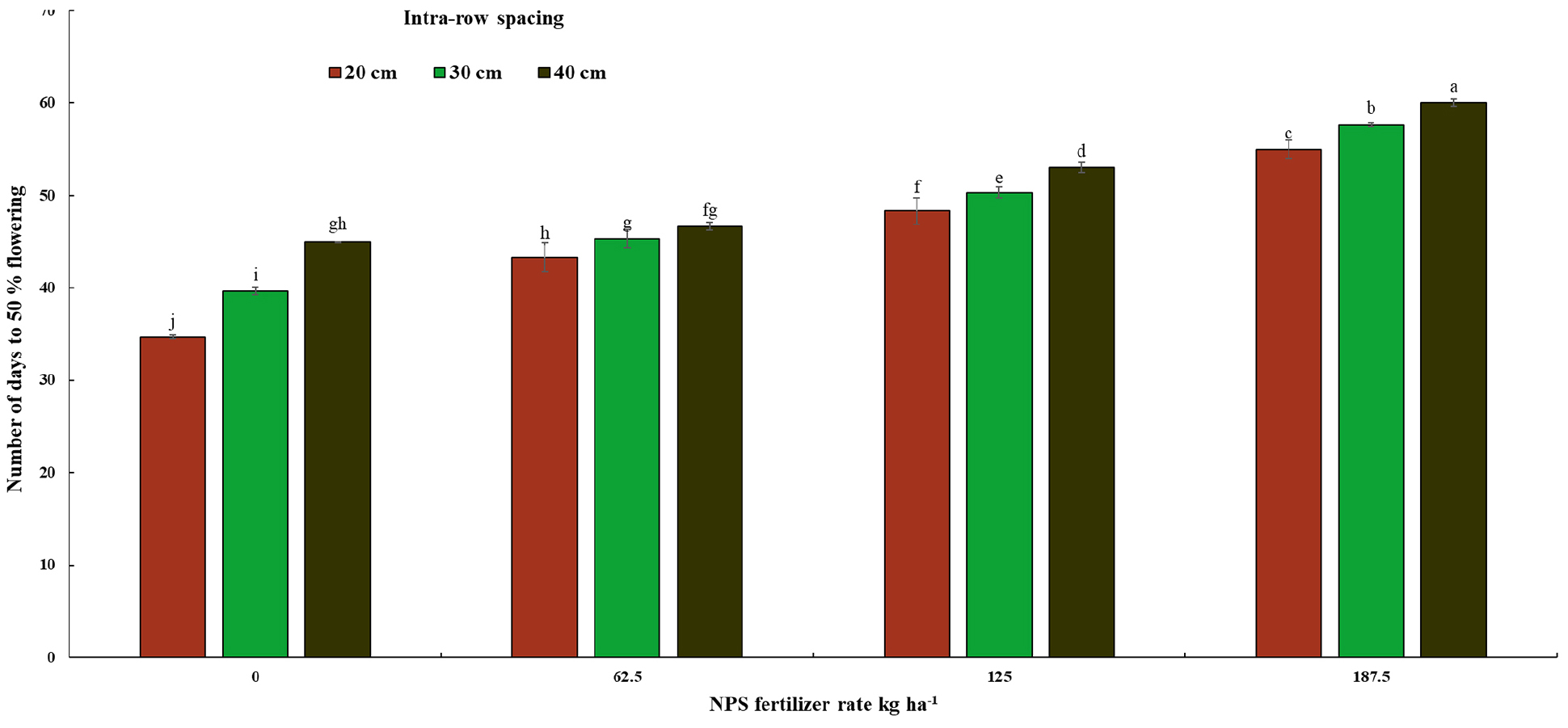
- Growth and Yield Response of Okra to NPS Fertilizer Rates and Plant Density in Jimma, Southwestern Ethiopia
- Lam Jock Tang, Amsalu Nebiyu, John Barnabas, Minwoo Baek, Shimeles Tilahun, Derbew Belew
- Okra, Abelmoschus esculentus L. (Moench), is an important vegetable crop in the Malvaceae family, recognized for its substantial nutritional and economic value. …
- Okra, Abelmoschus esculentus L. (Moench), is an important vegetable crop in the Malvaceae family, recognized for its substantial nutritional and economic value. Despite its potential, okra remains under-utilized, largely due to limited information on optimal agronomic practices. This study was conducted at the research premises of Jimma University College of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine (JUCAVM) to evaluate the effects of NPS fertilizer rates and plant population density on the growth, yield, and yield components of okra. The experiment consisted of three intra-row spacings (20, 30, and 40 cm) combined with four NPS fertilizer rates (0, 62.5, 125, and 187.5 kg ha-1). The results demonstrated that both NPS fertilizer rate and plant density significantly influenced key growth parameters, yield attributes, and pod yield of okra. A significant interaction between NPS fertilizer and plant density was observed for days to 50% flowering and the number of leaves per plant. The longest time to 50% flowering (60 days) occurred under the combination of 187.5 kg NPS ha-1 and 40 cm intra-row spacing, while the shortest (34.66 days) was recorded with 0 kg NPS ha-1 and 20 cm spacing. The maximum number of leaves (28.23) was obtained from 125 kg NPS ha-1 combined with 30 cm spacing. In addition, days to 50% pod set, plant height, length of the pod-bearing zone, number of branches, number of pods, pod length, fresh and dry pod weight, pod yield, and crop stand were significantly affected by the main effects of fertilizer rate and plant population. Overall, the application of 125 kg NPS ha-1 with an intra-row spacing of 30 cm resulted in better growth and maximum pod yield of the Amola okra variety under Jimma conditions. Further studies across diverse locations and seasons are recommended to confirm and strengthen these findings. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
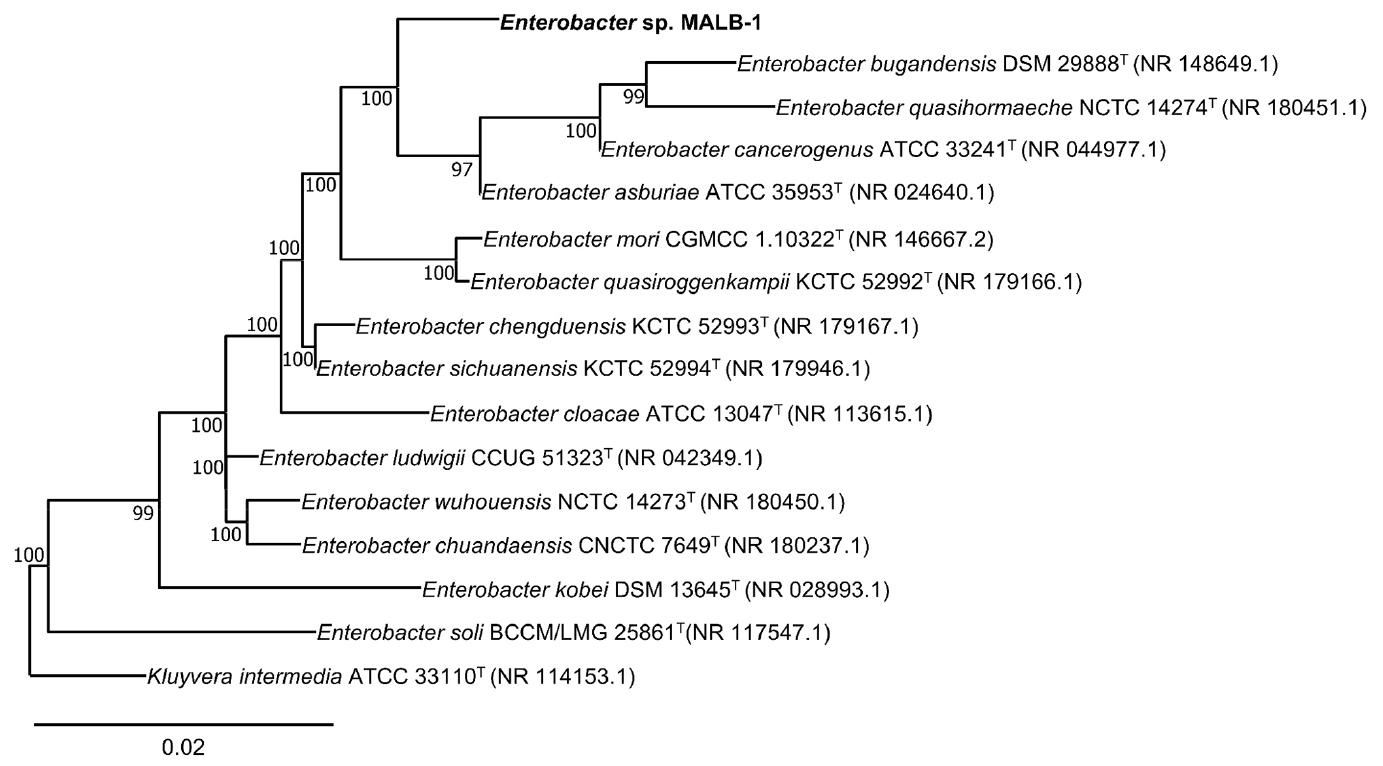
- Genomic and Phenotypic Characterization of Enterobacter sp. MALB-1 Isolated from Monochamus alternatus for Plant Growth-Promoting Potential and Safety Assessment
- Gang Hoon Lee, Jun Ho Lee, Tae Yun Choi, Seo Jun Lee, Saeyoull Cho
- In this study, we isolated a plant growth-promoting bacterium, designated Enterobacter sp. MALB-1, from the gut of Monochamus alternatus. A polyphasic …
- In this study, we isolated a plant growth-promoting bacterium, designated Enterobacter sp. MALB-1, from the gut of Monochamus alternatus. A polyphasic taxonomic approach demonstrated that while MALB-1 belongs to the genus Enterobacter, it represents a genetically and phenotypically distinct lineage. Whole-genome analysis revealed average nucleotide identity (ANI) values of 86.7-88.2% and digital DNA-DNA hybridization (dDDH) values of 31.8-34.7% with closely related type strains, which are significantly below the thresholds for species delineation. Genomic functional annotation identified a diverse repertoire of genes involved in nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization, and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) biosynthesis, highlighting its potential as a biofertilizer. Phenotypically, MALB-1 exhibited robust adaptability to agricultural stress conditions, including broad pH (5-9) and salinity tolerance (0-5%), and possessed a versatile metabolic profile capable of utilizing various root exudate components. Importantly, a comprehensive safety assessment was conducted to address concerns regarding the opportunistic pathogenicity of the genus. Although genomic screening detected putative virulence factors and antibiotic resistance genes, phenotypic susceptibility assays confirmed that MALB-1 is susceptible to key therapeutic antibiotics, including ampicillin, kanamycin, and norfloxacin. This distinctive susceptibility profile, in stark contrast to the multidrug-resistant phenotypes of related Enterobacter strains, suggests a manageable safety risk. Collectively, these findings position Enterobacter sp. MALB-1 as a promising, safe, and efficient candidate for agricultural application. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
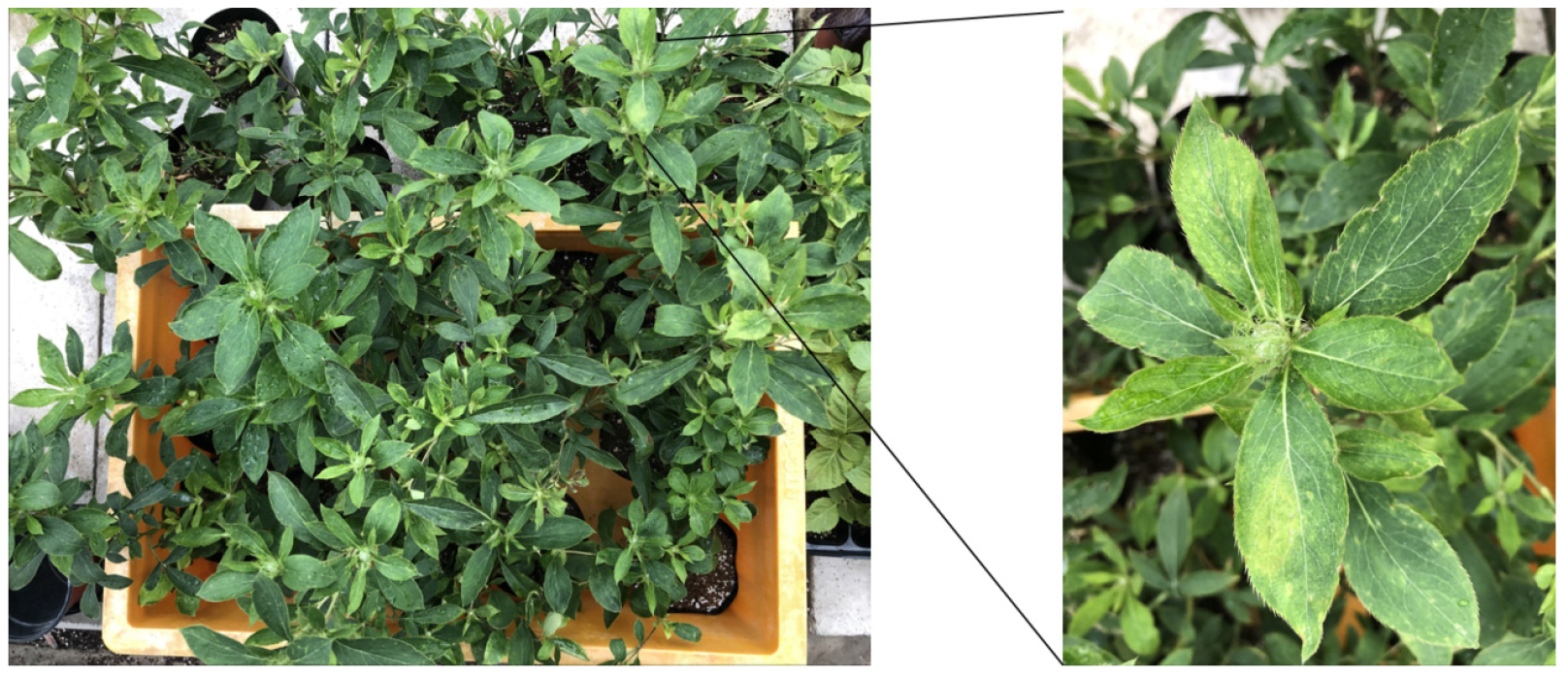

- Characterization of the New Cucumber Mosaic Virus Isolated from Atractylodes macrocephala
- Dongjoo Min, Gyeong Geun Min, Jisoo Park, Chaemin Shin, Jisu Kim, Suk Hyun Park, Ju-Yeon Yoon, Rae-Dong Jeong, Hangil Kim, Jin-Sung Hong
- Atractylodes macrocephala is a medicinal plant belonging to the genus Atractylodes, and it is widely cultivated in China and South Korea. …
- Atractylodes macrocephala is a medicinal plant belonging to the genus Atractylodes, and it is widely cultivated in China and South Korea. To date, five viruses have been reported to infect A. macrocephala. In this study, A. macrocephala plants showing distortion symptoms were collected in Chuncheon, South Korea, followed by RT-PCR analysis using primer sets specific to these five viruses as well as primer sets targeting seven commonly occurring virus genera in South Korea. RT-PCR result revealed an amplicon of the expected size only with Cucumovirus-specific primers, and sequence analysis of the amplified product confirmed infection by cucumber mosaic virus (CMV). The newly identified isolate was designated CMV-Atm. CMV isolates from A. macrocephala have previously been reported in both China and South Korea. Therefore, the biological and molecular characteristics of CMV-Atm were compared with those of previously reported A. macrocephala-derived CMV isolates. CMV-Atm exhibited distinct pathogenicity and host responses compared with the previously identified isolates, although its phylogenetic analysis indicated high sequence similarity with them. Collectively, these findings suggest that CMV-Atm is genetically conserved among other A. macrocephala-infecting CMV isolates but displays unique symptom expression, implying subtle adaptations in its host-pathogen interactions. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
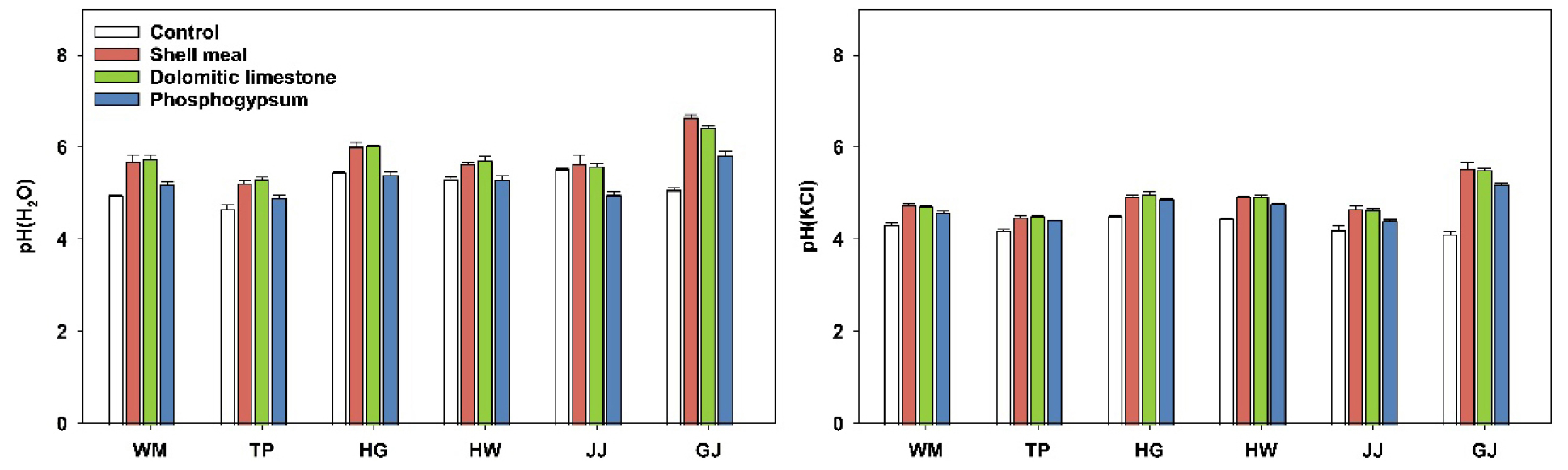
- Phosphogypsum as a Soil Amendment for Aluminum Detoxification and Sulfur Supply in Volcanic Ash Soils of Jeju Island: An Incubation Experiment
- Hosung Lee, Young-Hun Hyun, Won-Pyo Park
- In this study, we investigated the potential of phosphogypsum as a soil amendment for aluminum detoxification and sulfur supply in Jeju volcanic …
- In this study, we investigated the potential of phosphogypsum as a soil amendment for aluminum detoxification and sulfur supply in Jeju volcanic ash soils compared to shell meal and dolomitic limestone. Soil samples were collected from four black volcanic ash Andisols (Wimi, Topyeong, Hangyeong, and Hangwon series) and two non-Andisols: a very dark brown soil (Jeju series) and a dark brown soil (Gangjeong series). An incubation experiment was conducted for 30 days at 25°C under controlled conditions after applying amendments to each soil at a rate equivalent to 200 kg per hectare, adjusted for the alkalinity of each amendment. All soil amendments ledcrease in soil pH and total content of exchangeable cations compared with the untreated control, and shell meal and dolomitic limestone produced a relatively greater increase in pH (H2O), reflecting their liming properties. In contrast, phosphogypsum treatment resulted in the highest exchangeable calcium (Ca) and sulfur (S) contents, accompanied by a marked decrease in the exchangeable aluminum (Al) content and Al saturation in most soils. In Andisols with high Al and Fe contents, phosphogypsum application increased adsorbed S, indicating enhanced S retention and a greater potential for long-term S supply. In the non-Andisol Gangjeong, sulfur derived from phosphogypsum was retained mainly in exchangeable forms, suggesting that phosphogypsum can function as a readily plant-available sulfur source in this soil. Overall, these results indicate that although the liming effect of phosphogypsum on soil pH is weaker than that of shell meal and dolomitic limestone, phosphogypsum can be effectively used as a soil amendment in Jeju soils by alleviating Al toxicity in Andisols and improving soil chemical properties and plant-available S supply across contrasting soil types. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
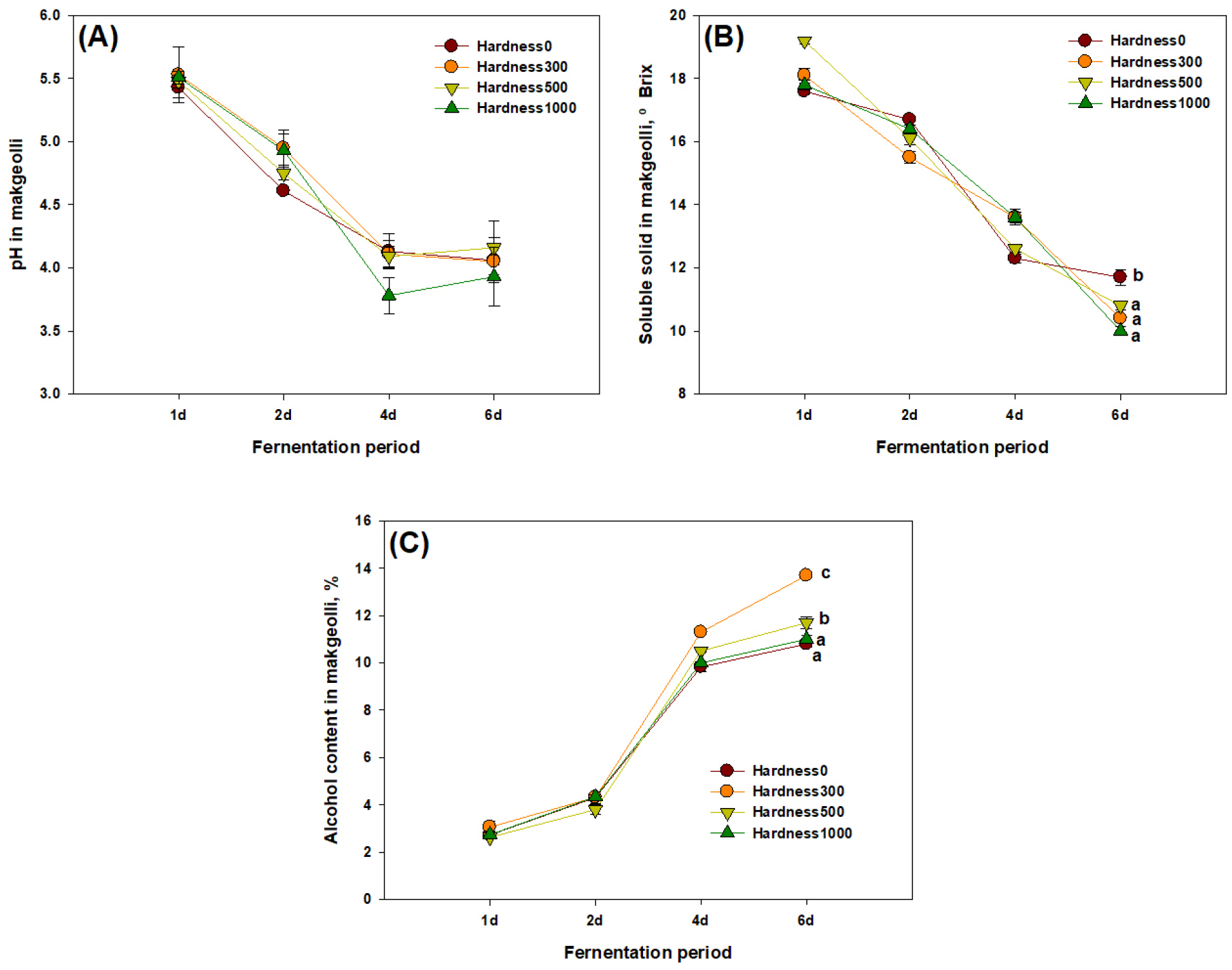
- Fermentation Properties of SC101 Starter Makgeolli with Deep Sea Water and Cacao Powder
- Hyun-Soo Yun, Taehui Yang, In-Pyo Jeon, Dae-Hee Lee, Jea-Man Sim, Sung-Ho Cho, Se-Jin Oh
- Recently, the domestic liquor market in South Korea has seen a period of continuous expansion, particularly in traditional fermented liquors, such as …
- Recently, the domestic liquor market in South Korea has seen a period of continuous expansion, particularly in traditional fermented liquors, such as makgeolli. This study evaluated the fermentation properties of makgeolli produced using the SC101 starter (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), deep sea water (DSW), and cacao powder (CP). Fermentation was conducted for 6 d at 25°C using 0.6% starter, 0.05% purified enzyme or 50% malt, and 200 mL of water per 100 g of rice. Furthermore, the effects of adding CP and DSW (adjusted to water hardness from 0 to 1,000 mg/L as CaCO3) were investigated. The addition of CP to makgeolli significantly increased alcohol production, with the purified enzyme treatment showing higher efficiency compared to that of malt. DSW supplementation served as a source of macro- and micro-nutrients, resulting in 21% and 8% improvements in alcohol yield at hardness levels of 300 and 500 mg/L as CaCO3, respectively, along with the highest yeast population observed during fermentation. However, increasing the hardness to 1,000 mg/L as CaCO3 reduced both the yeast population and alcohol production. Thus, the appropriate use of CP and DSW enhances the fermentation efficiency of makgeolli and contributed to the development of regionally specialized traditional liquors. - COLLAPSE
-
Notice
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Agricultural, Life and Environmental Sciences
Journal of Agricultural, Life and Environmental Sciences
 Journal of Agricultural, Life and Environmental Sciences
Journal of Agricultural, Life and Environmental Sciences



